Reporting frameworks are invaluable tools for education and learning development managers in the healthcare sector. They facilitate continuous improvement, enabling health professionals to learn from each other and from the healthcare system itself. This article explores how these frameworks can be used to enhance learning and development programs, offering practical advice for implementation.
What is a Reporting Framework?
A reporting framework provides a structured approach for collecting, analysing, and disseminating information. In healthcare, this often involves compiling health information to assess performance, identify risks and opportunities, and guide decision-making. Reporting frameworks help standardise the reporting landscape, ensuring that health services and professionals can reliably track and improve upon care outcomes.
How are Reporting Frameworks Used in Healthcare?
In the healthcare sector, reporting frameworks are used to monitor and improve the quality of care provided by health professionals. They facilitate the collection of data related to patient outcomes, staff performance, and operational efficiency, allowing for informed improvements in primary care, public health, and other areas of the healthcare system.
How Can Reporting Frameworks Enhance Learning and Development Programs?
Reporting frameworks enhance learning and development programs by providing structured feedback and data-driven insights. They enable health professionals to identify areas for improvement, benchmark their performance, and engage in continuous professional development. This data-centric approach ensures that learning initiatives are aligned with the needs of healthcare providers and patients.
Examples of Reporting Frameworks in Healthcare
Reporting frameworks in healthcare vary widely, reflecting the diversity of care settings and objectives. These frameworks play a crucial role in ensuring quality and accountability across health services. Below are detailed examples demonstrating the range and focus of reporting frameworks within the healthcare sector.
- National Health Performance Framework: Monitors the performance of health services against national standards, focusing on efficiency, safety, and quality of care.
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission's Reporting Guidelines: Provides a comprehensive set of standards for the quality of aged care services, ensuring the safety and wellbeing of older Australians.
- Healthcare Associated Infection (HAI) Reporting Framework: Aims to reduce infections acquired in healthcare settings, enhancing patient safety through rigorous monitoring and reporting of infection rates.
- Mental Health Services Reporting Framework: Focuses on the delivery and outcomes of mental health services, aiding in the improvement of mental health care through detailed data analysis and reporting.
How to Create a Reporting Framework
Creating a reporting framework involves defining objectives, selecting relevant metrics, and establishing processes for data collection, analysis, and reporting. It's essential to engage stakeholders in the development process to ensure the framework meets the needs of all parties involved in healthcare delivery.
Steps to Build a Reporting Framework for Your L&D Program
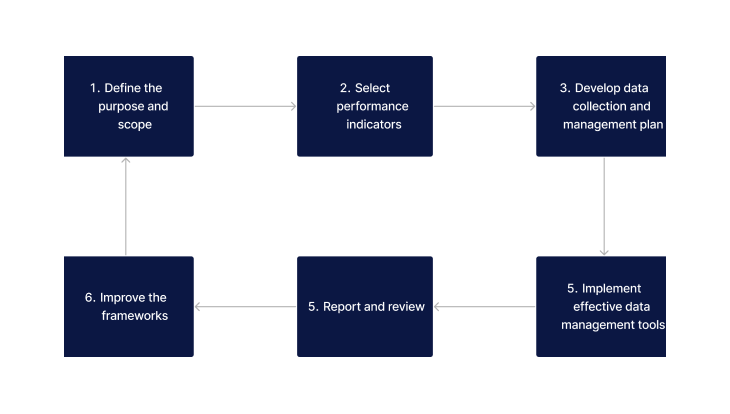
Creating an effective reporting framework requires careful planning and execution. The following steps outline a comprehensive approach to building a framework that is robust, flexible, and capable of driving improvement in healthcare services.
- Define the framework's purpose and scope: This ensures there is alignment with organisational goals.
- Select performance indicators: These should accurately reflect key areas of interest and potential improvement.
- Develop a data collection and management plan: to ensure consistency and reliability of information.
- Implement tools for effective data analysis: Support decision-making and insight generation with quantifiable and visual support.
- Reporting and review: Establish a regular schedule for to maintain momentum and focus on improvement.
- Improve the frameworks: Take action based on the findings to ensure meaningful use of the information gathered.
Want a healthcare LMS that can support learning plans around reporting frameworks?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Benefits and Negatives of Designing Reporting Frameworks
While reporting frameworks are indispensable for quality improvement, they come with their own set of challenges and considerations. Understanding these benefits and negatives is key to developing effective frameworks.
| Benefits | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Enhanced transparency and accountability in healthcare delivery. | Can lead to data overload, causing analysis paralysis. |
| Supports data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement. | Requires significant resources for implementation and maintenance. |
| Improves patient outcomes by identifying areas for improvement. | Potential for narrow focus on quantifiable metrics at the expense of qualitative insights. |
| Facilitates benchmarking and best practice sharing across healthcare organisations. | May create resistance or apprehension among staff wary of surveillance or punitive measures. |
| Enables targeted resource allocation to areas of most need or potential impact. | Risk of becoming outdated if not regularly updated to reflect current standards and practices. |
Tips for Designing Reporting Frameworks for Learning and Development Programs
Designing effective reporting frameworks for learning and development within the healthcare sector requires attention to several key principles. These tips ensure the framework not only meets current needs but is also adaptable to future changes.
- Engage with stakeholders early in the design process to gather insights and ensure the framework meets diverse needs.
- Focus on user experience to increase engagement and ensure ease of use, from data entry to report generation.
- Implement a modular and flexible design that allows for adjustments and expansions as healthcare practices evolve.
- Provide clear guidelines and training to support effective use of the framework, ensuring users can easily interpret and act on the data.
Related Resources
- Guide to Mandatory Training
- LMS in Healthcare: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- What Are Learning Analytics?
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Collection for Learning Analytics
- What Are the Key Learning Analytics Metrics?
- How to Create a Culture of Continuous Learning
- Guide to Compliance Training (for Healthcare Managers)
- Guide to Building a Competency Framework for Skill Development
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- A Guide to Personalised Learning in Healthcare
Conclusion
Effective reporting frameworks are vital tools in the continuous effort to improve healthcare education and practice. By carefully considering the design, implementation, and iterative refinement of these frameworks, healthcare educators and administrators can enhance learning outcomes, support professional development, and ultimately contribute to the delivery of higher quality care.
References
- World Health Organization. (2020). Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology for Healthcare-associated Infection (HAI) Reporting Framework. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission. (2021). Aged Care Quality Standards. Retrieved from https://www.agedcarequality.gov.au/aged-care-quality-standards
- Department of Health, Australian Government. (2022). National Health Performance Framework. Canberra: Department of Health.
- Mental Health Commission. (2018). National Mental Health Services Reporting Framework. Retrieved from https://www.mentalhealthcommission.gov.au/Monitoring-and-Reporting/national-reports



