What are Learning Analytics?
Learning analytics involve the measurement, collection, analysis, and reporting of data about learners and their contexts, for purposes of understanding and optimising learning and the environments in which it occurs. Analytics tools play a crucial role in deciphering this data, aiding educational institutions in supporting student success.
What Are Learning Outcomes?
Learning outcomes are statements that describe the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values staff are expected to acquire from the learning activity. They are central to the learning process, guiding the design of curricula and the assessment of learner progress.
They include:
- Knowledge Acquisition: Learning outcomes detail the specific facts, theories, and principles that learners should understand following a course or module.
- Skills Development: They outline the practical skills or competencies staff are expected to develop, such as analytical thinking, problem-solving, or technical abilities relevant to their field of study.
- Attitude and Value Formation: Learning outcomes also encompass the attitudes, ethical standards, and values learners should adopt, highlighting the importance of professional behavior and critical reflection.
- Behavioral Changes: They aim for observable changes in behavior, indicating the application of acquired knowledge and skills in real-world contexts or simulated environments.
- Assessment Benchmarks: Learning outcomes serve as benchmarks for evaluating student progress and the effectiveness of the curriculum, guiding educators in measuring achievement through exams, projects, and other forms of assessment.
How are Learning Outcomes Used in Healthcare?
In healthcare education, learning outcomes provide a framework for assessing staff skills and developing strategies for skill enhancement. They align with the needs of the health system, ensuring that learning activities are relevant and impactful.
- Defining Educational Goals: In healthcare, learning outcomes provide a clear definition of what staff, including nurses, doctors, and allied health professionals, are expected to learn, ensuring that educational programs align with the requirements of the health system.
- Guiding Curriculum Development: Learning outcomes are used to design curricula that meet the specific needs of healthcare professionals, focusing on relevant skills and knowledge that improve patient care and operational efficiency.
- Enhancing Staff Engagement: By clearly outlining expected outcomes, healthcare organisations can increase engagement among staff by providing a clear path for professional development and achievement.
- Facilitating Assessment and Evaluation: Learning outcomes allow for the effective assessment of healthcare staff's skills and knowledge, helping to identify areas for improvement and measuring the impact of training programs.
- Supporting Continuous Professional Development: They serve as benchmarks for continuous learning, helping healthcare professionals keep pace with the latest practices, technologies, and regulatory requirements.
- Improving Patient Care: Ultimately, the application of learning outcomes in healthcare education leads to improved patient care and outcomes, as staff are better prepared to apply their knowledge and skills in clinical settings.
Examples of Learning Analytics Being Used to Improve Learning Outcomes
There are several educational institutions have successfully applied learning analytics to enhance learning outcomes. For example, online learning platforms use analytics to personalise the learning experience, tracking engagement and performance to adjust content delivery.
- Personalised Learning Paths: Online platforms utilise learning analytics to create customised learning experiences for each student. By analysing data on staff's past performance and learning preferences, these platforms can tailor content, recommend resources, and adjust difficulty levels to meet individual needs.
- Early Identification of At-Risk Staff: Institutions employ analytics to monitor student engagement and performance in real-time, allowing for the early identification of staff who are at risk of falling behind. This enables timely intervention with additional support or tailored learning strategies to help them succeed.
- Enhanced Feedback Mechanisms: Learning analytics provide detailed insights into student learning processes, enabling educators to offer more targeted and meaningful feedback. This can help staff understand their strengths and weaknesses, and how to improve their learning strategies.
- Optimisation of Learning Resources: Analytics can reveal which learning materials and activities are most effective, allowing institutions to refine their course content and instructional methods to better align with student needs and learning outcomes.
- Improving Course Design: By analysing patterns and trends in data, educators can identify areas of the curriculum that may need adjustment. This could include the introduction of new topics, reordering material for better logical progression, or removing outdated content.
- Supporting Staff Development: Analytics can also inform the professional development of teaching staff, identifying areas where additional training or resources could enhance teaching effectiveness and, consequently, learning outcomes.
How Can I Use Learning Analytics to Improve Learning Outcomes?
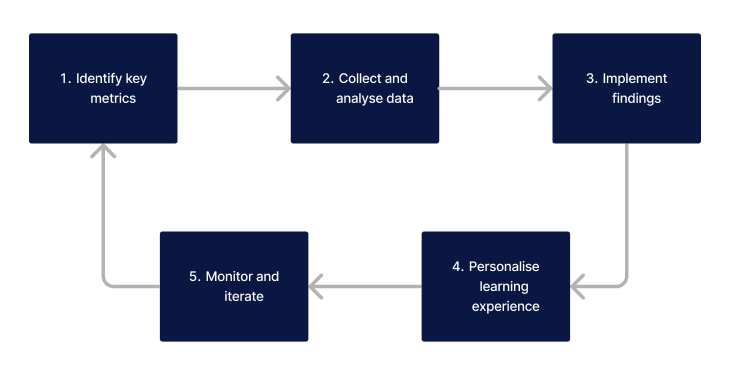
Application of learning analytics to improve learning outcomes in healthcare involves the following:
- Identify Key Metrics: Determine which data points are most indicative of learning success within your context.
- Collect and Analyse Data: Use analytics tools to gather and examine data about learners and their engagement with the material.
- Implement Findings: Apply insights from the data to modify learning activities, environments, and strategies for better outcomes.
- Personalise Learning Experiences: Utilise analytics to tailor the learning journey for individual students based on their progress, strengths, and areas for improvement. This personalised approach can enhance engagement and efficacy.
- Monitor and Iterate: Continuously track the impact of changes on learning outcomes and student satisfaction. Use this ongoing feedback to refine your approach, ensuring that the learning experience remains dynamic and responsive to student needs.
Want a healthcare LMS that can support your team improve their learning outcomes?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Tips for Using Learning Analytics to Improve Learning Outcomes in Healthcare
When adopting learning analytic strategies, healthcare professionals and educators should consider the following key factors to ensure effective learning outcomes.
These include:
- Focus on staff engagement and contextual learning: Develop content specifically tailored for healthcare settings to make learning more relevant and engaging. This approach helps in retaining crucial information and applying it effectively in clinical situations.
- Utilise analytics for continuous improvement: Continuously analyse educational outcomes and feedback to refine and adapt learning strategies. This dynamic approach ensures that training remains responsive to both the evolving needs of healthcare professionals and advancements in medical practice.
- Intergrate with clinical practice: Align educational content closely with practical clinical experiences. By analysing performance in simulations and real-world scenarios, educators can adjust training to better prepare staff for the challenges they will face in their roles.
- Adopt predictive analytics: Use data analysis to forecast future learning needs and challenges within the healthcare sector. Predictive insights can guide the development of forward-thinking educational programs that pre-emptively address upcoming industry shifts and skill requirements.
- Encourage self-directed learning: Provide learners with access to their own learning data. This empowers them to take control of their learning process, identify their own strengths and weaknesses, and tailor their learning experiences accordingly.
- Leverage data for personalised learning: Use analytics to create personalised learning paths for healthcare staff.
Strategies to Improve Learning Outcomes With Learning Analytics
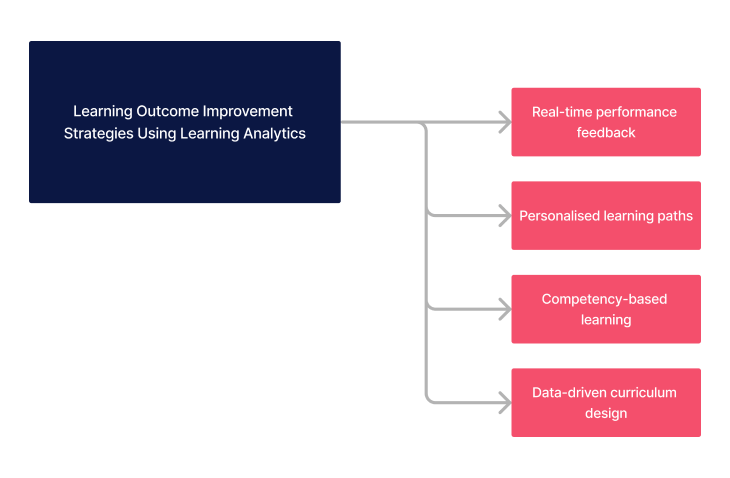
Before implementing strategies, it's essential to have a clear understanding of the skills required in healthcare contexts. Strategies include assessing staff skills through analytics and developing targeted learning activities that address identified gaps.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time performance feedback | Use learning analytics to provide immediate feedback on learner performance, allowing for quick adjustments and targeted support where needed. |
| Personalised Learning Paths | Develop individualised learning plans based on analytics, catering to the unique strengths and weaknesses of each learner. |
| Competency-Based Learning | Focus on achieving specific competencies critical to healthcare, using analytics to track progress and guide learning activities. |
| Data-Driven Curriculum Design | Revise and enhance curriculum content and structure based on insights gained from learning analytics, ensuring it meets current healthcare demands and learner needs. |
Related Resources
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Collection for Learning Analytics
- What Are Learning Analytics (A Guide for Healthcare)
- How Do I Use Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping?
- How Can I Use Learning Analytics for Employee Onboarding?
- How Can I Use Learning Analytics for Employee Retention?
- How to Use 'Nudge Theory' to Encourage Completion of Outstanding Learning
Conclusion
Learning analytics offer powerful tools for enhancing learning outcomes in healthcare education. By focusing on data-driven insights, educators can create more effective and engaging learning experiences that meet the needs of both learners and the healthcare system.
References
- Rogers, B, Baker, KA & Franklin, AE, 2020, 'Learning outcomes of the observer role in nursing simulation: a scoping review', Clinical Simulation in Nursing, vol.49, pp.81-89.
- Chan, AK, Botelho, MG & Lam, OL, 2019, 'Use of learning analytics data in health care–related educational disciplines: systematic review', Journal of medical Internet research, vol.21, no.2, p.e11241.
- Banihashem, SK, Aliabadi, K, Pourroostaei Ardakani, S, Delaver, A & I Nili Ahmadabadi, M., 2018, 'Learning analytics: A systematic literature review', Interdisciplinary Journal of Virtual Learning in Medical Sciences, vol.9, no.2.
- Rehman, A, Naz, S, & Razzak, I, 2022, 'Leveraging big data analytics in healthcare enhancement: trends, challenges and opportunities', Multimedia Systems, vol.28, no.4, pp.1339-1371.
- Joksimović, S, Kovanović, V, and Dawson, S, 2019, 'The journey of learning analytics', HERDSA Review of Higher Education, vol.6, pp.27-63.



