What is Peer Feedback?
Peer feedback involves staff or colleagues providing feedback on each other's work. It's a critical component of the learning process, fostering a collaborative learning environment where individuals can share and receive feedback. This process encourages learners to engage critically with their peers' work, offering specific feedback to aid improvement.
How to Ask for Peer Feedback
Effectively asking for peer feedback necessitates a strategic approach. It's about being clear and direct with your requests, ensuring that you pinpoint exactly what aspects of your work you want feedback on. This specificity helps your peers provide targeted, useful feedback that can lead to significant improvements in your work.
How to Give Peer Feedback
Giving peer feedback effectively is an art. It requires balancing honesty with empathy, ensuring that your critique is constructive and aimed at fostering growth. Providing specific, actionable advice, rather than vague or overly critical comments, can transform feedback into a powerful tool for learning and development.
Examples of Peer Feedback
Providing specific examples of peer feedback is instrumental in illustrating how constructive critique can be delivered. Each example below demonstrates how to address different aspects of work, ensuring feedback is not only insightful but also empowers improvement.
Presentation Skills:
"Your eye contact and pacing were excellent, enhancing your engagement with the audience. Consider using more visual aids to underscore key points."
Writing Clarity:
"Your argument is compelling, but some points could be clearer. Try breaking down complex ideas into shorter sentences."
Problem-Solving Approaches:
"Your approach to solving the issue was creative. Perhaps exploring alternative solutions could also provide valuable insights."
How Can Peer Feedback Enhance Learning?
Peer feedback enhances learning by providing learners with insights from their peers, which can offer new perspectives and ideas. This process helps learners to reflect on their own work and to consider other approaches to learning and problem-solving.
How to Use Peer Feedback to Enhance Learning
To maximise the benefits of peer feedback, it should be integrated into the learning process as a regular practice. Encouraging learners to give and receive feedback regularly helps to create a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Steps to Use Peer Feedback to Enhance Learning
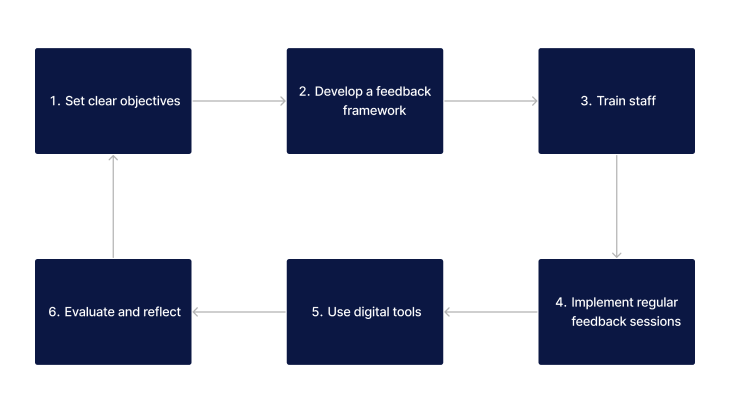
Effective integration of peer feedback into the learning process requires a structured approach. The steps outlined below are designed to facilitate a comprehensive peer feedback mechanism, ensuring that feedback is not just collected but also effectively utilised for learning enhancement.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve with peer feedback within your course or project.
- Develop a Feedback Framework: Create guidelines and criteria for giving constructive feedback to ensure consistency and quality.
- Train Staff: Offer training sessions on effective communication and feedback techniques to enhance the quality of peer interactions.
- Implement Regular Feedback Sessions: Schedule regular sessions for peer feedback, making it a routine part of the learning process.
- Use Digital Tools: Leverage online platforms for peer feedback submission, allowing for both synchronous and asynchronous communication.
- Evaluate and Reflect: Encourage participants to reflect on the feedback received and to consider how it can be applied to their work.
Benefits and Negatives to Peer Feedback to Enhance Learning
The implementation of peer feedback in educational settings brings with it a range of benefits and potential negatives. Understanding these can help educators and learners navigate the feedback process more effectively, ensuring that the benefits are maximised while the negatives are minimised.
| Benefits | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Critical Thinking and Creativity: Peer feedback encourages staff to think critically about their own and others' work. By evaluating the work of peers, staff learn to identify strengths and weaknesses, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject matter. | Quality and Reliability Concerns: The quality of peer feedback can vary significantly, depending on the staff' ability to assess work accurately and constructively. |
| Increased Engagement and Motivation: The interactive nature of peer feedback increases student engagement. When learners know their peers will review their work, they are often more motivated to put forth their best effort. | Potential for Miscommunication and Conflict: Without proper guidance on how to give and receive feedback, there's a risk of miscommunication. |
| Development of Soft Skills: Participating in peer feedback sessions helps staff develop essential soft skills, such as communication, empathy, and the ability to receive and apply feedback constructively. | Emotional Impact on Staff: Receiving negative feedback, even when constructive, can be challenging. Staff may feel discouraged or defensive, especially if they perceive the feedback as a personal attack rather than an opportunity for growth. |
| Fosters a Supportive Learning Environment: Peer feedback can create a sense of community and support among learners. It encourages a learning culture where staff feel comfortable sharing their ideas and are open to learning from each other. | Bias and Subjectivity: Peer feedback is inherently subjective, with personal biases potentially influencing evaluations. staff might favour friends or be influenced by preconceptions about their peers' abilities. |
Tips for Using Peer Feedback to Enhance Learning
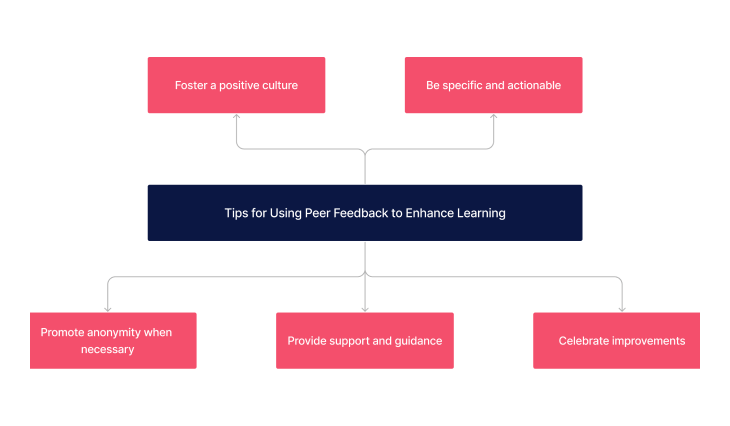
Maximising the effectiveness of peer feedback involves adopting certain best practices. These tips are designed to ensure that feedback serves as a catalyst for improvement and learning, fostering a positive and constructive feedback culture.
- Foster a Positive Culture: Cultivate an environment where feedback is seen as a valuable part of learning.
- Be Specific and Actionable: Encourage feedback that is detailed and directly applicable to the work being reviewed.
- Promote Anonymity When Necessary: Anonymous feedback can reduce bias and encourage honesty, especially in sensitive contexts.
- Provide Support and Guidance: Offer resources and support to help learners understand how to use feedback constructively.
- Celebrate Improvements: Acknowledge and celebrate the application of feedback and improvements made, reinforcing the value of the feedback process.
Related Resources
- What Are Learning Analytics?
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Collection for Learning Analytics
- What Are the Key Learning Analytics Metrics?
- Guide to Compliance Training (for Healthcare Managers)
- Guide to Building a Competency Framework for Skill Development
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- How Do I Use Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping?
- A Guide to Personalised Learning in Healthcare
Conclusion
Peer feedback, when implemented effectively, can significantly enhance the learning process by fostering an environment of mutual respect and continuous improvement. By incorporating peer feedback into teaching and learning strategies, educators can create a dynamic and engaging learning experience that benefits all participants.
References
- Chakarvati, P. (2023). Investigating the Effectiveness of Peer Feedback in Developing Critical Thinking Skills in Undergraduate Students. Journal of Education Review Provision, 2(3):91-95. DOI: 10.55885/jerp.v2i3.192
- Lai, C., Lin, H., Lin, R., & Tho, P. D. (2019). Effect of Peer Interaction among Online Learning Community on Learning Engagement and Achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET), 17(1), 66-77. DOI: http://doi.org/10.4018/IJDET.2019010105
- Lerchenfeldt, S., Kamel-ElSayed, S., Patino, G. et al. A Qualitative Analysis on the Effectiveness of Peer Feedback in Team-Based Learning. Medical Science Educator, 33, 893–902. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-023-01813-z



